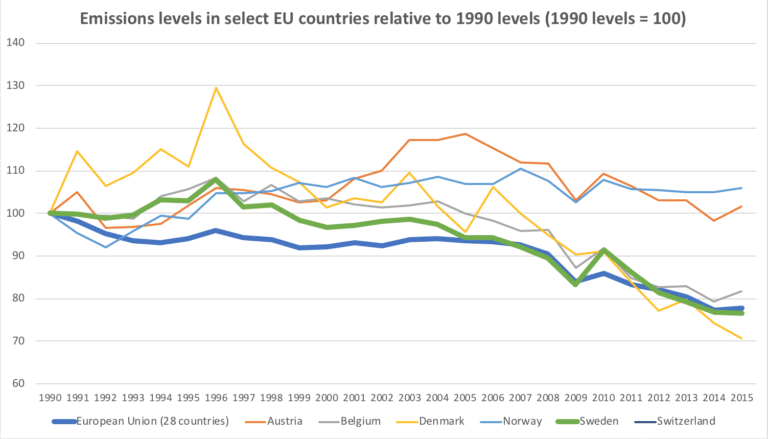
carbon tax vs cap and trade pros and cons
Cap-and-trade has one key environmental advantage over a carbon tax. 11 Price and Quantity.
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
Simply put the less fossil fuel used the less the tax affects the company.

. I believe carbon taxes are the better of the two options because it is simple and immediately causes companies and individuals of ways to reduce fuel and energy consumption. Carbon Tax vs. A carbon tax could force businesses and citizens to cut back carbon-intensive services and goods.
However a cap-and-trade policy offers its own advantages in that emissions allowances can be allocated so as to minimize the policys negative effects on competitiveness and prevent. However in reality they differ in many ways. We show that the various options are equivalent along.
You can do the same to cap-and-trade. It provides more certainty about the amount of emissions reductions that will result and little certainty about the price of emissions which is set by the emissions trading market. A carbon tax directly establishes a price on greenhouse gas emissionsso companies are charged a dollar amount for every ton of emissions they producewhereas a.
There is less agreement however among economists and others in the policy community regarding the choice of specific carbon-pricing policy instrument with some supporting carbon taxes and others favoring cap-and-trade mechanisms. Carbon taxes makes emitting carbon dioxide more expensive. Several analyses have claimed that a carbon tax is superior to cap and trade in terms of the ability to achieve a fair distribution of the policy burden between polluters firms and consumers to preserve international competitiveness or to avoid problems associated with the verification of emissions offsets.
How do the two major approaches to carbon pricing compare on relevant dimensions including but not limited to. Both reduce emissions by encouraging the lowest-cost emissions reductions and they do so without anyone needing to know beforehand when and where these emissions reductions will occur. A carbon tax has a major advantage over cap-and-trade and a hybrid version because it allows for carbon price certainty is less costly to administer and is a substantial source of revenue.
The revenue generated from the taxation will also assist Canadians by ultimately facilitating greener practices by subsidization and funding environmentally conscious research. Several analyses have claimed that a carbon tax is superior to cap and trade in terms of the ability to achieve a fair distribution of the policy burden between polluters firms and consumers to preserve international competitiveness or to avoid problems associated with the verification of emissions offsets This paper indicates that these. Theory and practice Robert N.
Each approach has its vocal supporters. April 9 2007 413 pm ET. The carbon tax system has been cited to both grow the economy.
Carbon Tax vs. It could start a race for lower emissions technologies which would give energy companies an edge on competitors. Yale Environment 360 Editor Roger Cohn asked eight climate policy experts all favoring controls but differing on cap-and-trade versus taxes to spell out their positions.
Here is the Econ 101 version of how the two work. To a first approximation cap-and trade is the equivalent of a carbon tax. For firm B the 3 tax is more than the 2 cost to reduce so B pays no tax and eliminates emissions.
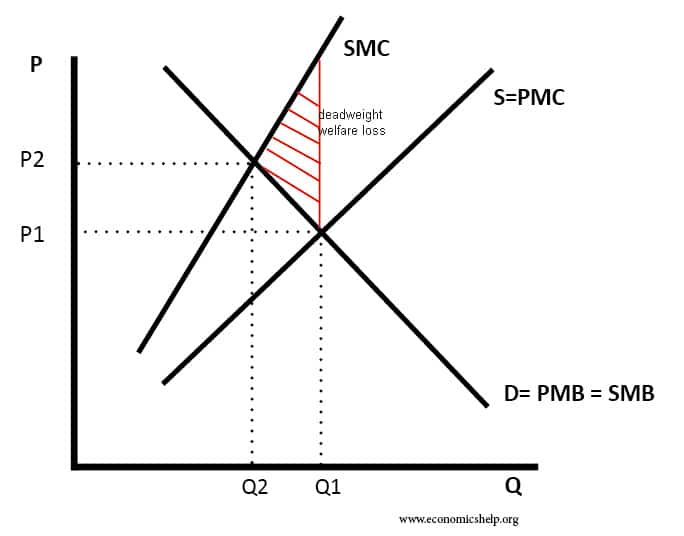
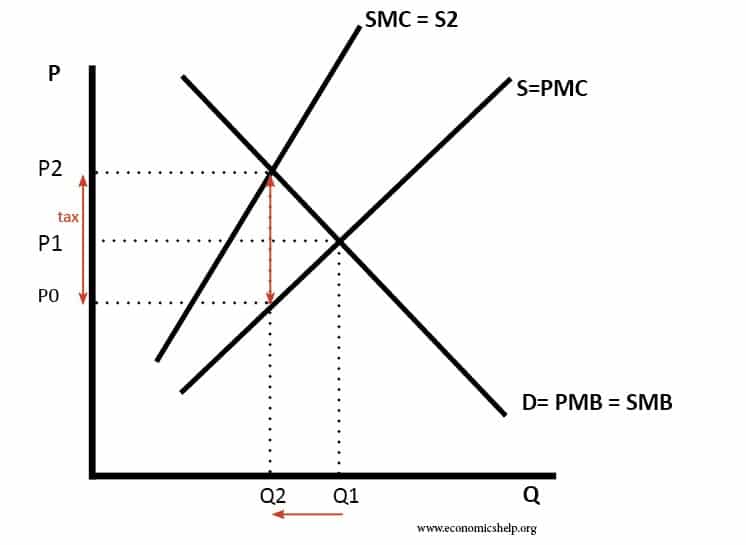
You can tweak a tax to shift the balance. Government sets a tax of 3 per ton of emissions. With a cap you get the inverse.
Cap-and-Trade systems limit the amount of carbon dioxide that gets emitted but gives little control to the price. In short there are sensible economic reasons for taking either side in the cap and trade vs. Plus some conservatives may be attracted to a carbon tax as an alternative to more EPA regulations.
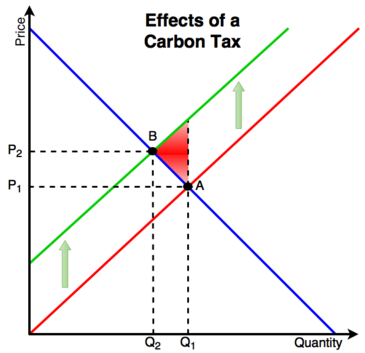
Those supporting a carbon tax argue that it is a better approach because it is. Before the policy the intersection of the supply and demand curves for. Both can be weakened.
A carbon tax sets the price of carbon dioxide emissions and allows the market to determine the quantity of emission reductions. No matter how much gets emitted a carbon tax makes the emission the same. Beyond helping prevent price volatility and reducing expected policy errors in the face of uncertainties exogenous pricing helps avoid problematic interactions with other climate policies and helps avoid large wealth.
The pros and cons of both approaches are neatly summarized in a May 7 posting at the Yale Environment 360 website. We examine the relative attractions of a carbon tax a pure cap-and-trade system and a hybrid option a cap-and-trade system with a price ceiling andor price floor. With a tax you get certainty about prices but uncertainty about emission reductions.
Stavins1 Harvard Kennedy School This paper compares the two major approaches to carbon pricing carbon taxes and cap and trade in the context of a possible future climate policy and does so. For firm A the 3 tax is less than the 4 cost to reduce so A pays the tax and does not reduce emissions. In certain idealized circumstances carbon taxes and cap-and-trade have exactly the same outcomes since they are both ways to price carbon.
A key finding is that exogenous emissions pricing whether through a carbon tax or through the hybrid option has a number of attractions over pure cap and trade. This can be implemented either through a carbon tax known as a price instrument or a cap-and-trade scheme a so-called quantity instrument. A carbon tax imposes a tax on each unit of greenhouse gas emissions and gives.
Those in favor of cap and trade argue that it is the only approach that can guarantee that an environmental objective will be achieved has been shown to effectively work to protect the environment at lower than expected costs and is politically more attractive. It seems inevitable that some day Congress will pass legislation meant to cut greenhouse-gas emissions. Finally the practicality of reducing emissions under a carbon taxation system is much more functional than the cap-and-trade program.
But the smart money seems to. 1 Effects of Emissions Trading and a Carbon Tax. As such they recommend applying the polluter pays principle and placing a price on carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
Carbon taxes vs. Cap and Trade. Carbon taxes and cap-and-trade programs share several major advantages over alternative policies.
Cap-and-trade sets the quantity of emissions reductions and lets the.

27 Main Pros Cons Of Carbon Taxes E C

Carbon Concentrations In The Northern Hemisphere Climate Change Change Climates
Carbon Tax Vs Emissions Trading Energy Education

Cap And Trade Vs Carbon Tax Youtube

Hale Denim Review Denim Style Hale

Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help

The Pros And Cons Of Carbon Taxes And Cap And Trade Systems Semantic Scholar

The Pros And Cons Of Carbon Taxes And Cap And Trade Systems Semantic Scholar

Yellen S Testimony Last Week Didn T Change Much In The Financial Markets Stock Markets Continue To Push Higher Financial Markets Financial News Stock Market
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
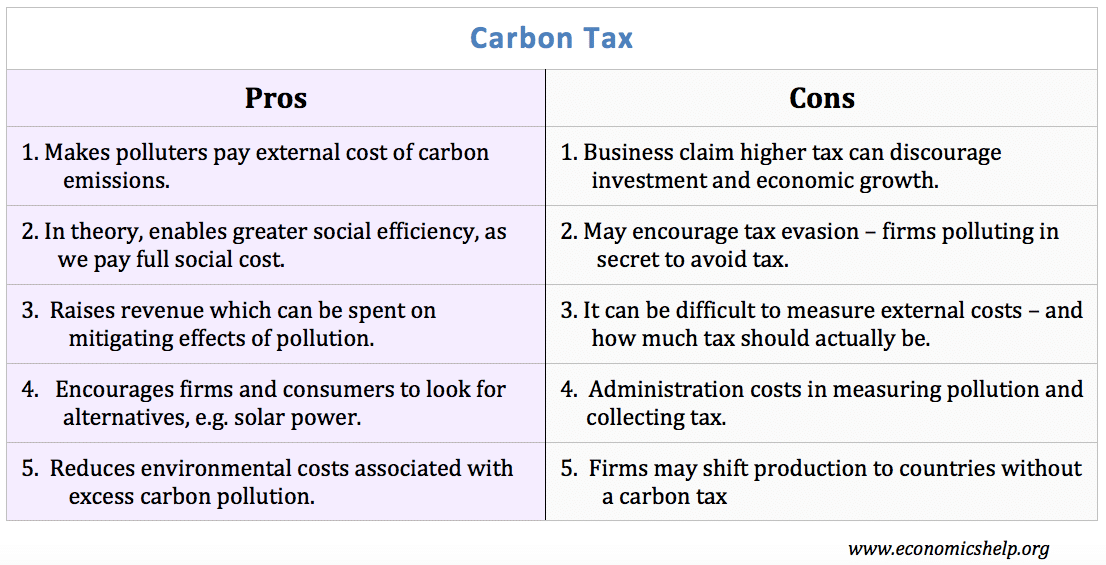
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
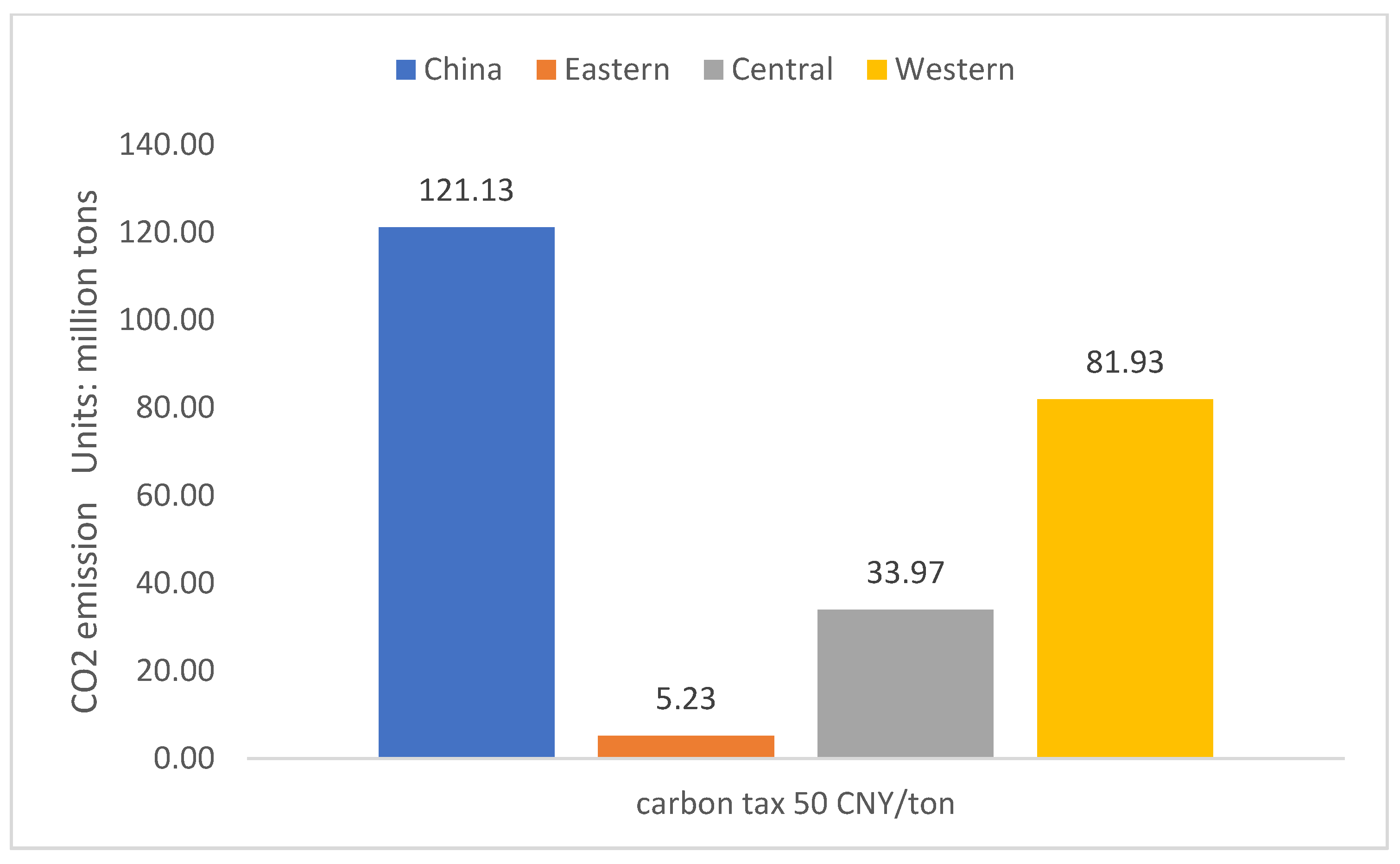
Sustainability Free Full Text How Does The Carbon Tax Influence The Energy And Carbon Performance Of China Rsquo S Mining Industry Html
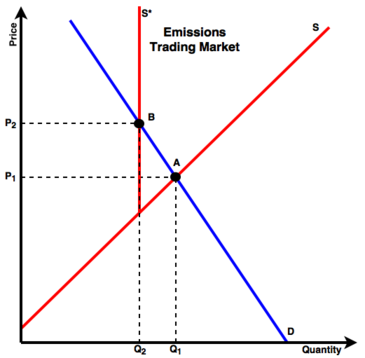
Carbon Tax Vs Emissions Trading Energy Education

Carbon Tax Definition How It Works Pros Cons

